The word ‘web design’ is a lot like the word ‘snow’ to an Eskimo Inuit. They say that the Unuit have over 50 words to describe the word snow, which makes sense given their relationship with the environment. They need to describe what type of snow is good for building with, to eat, dangerous icy snow, etc…
The problem most people have when it comes to ‘Web Design’ is that they are describing many different things with the same word.
Why is that you can pay $20/month to Wix for ‘web design’ or pay an agency $20,000 or more for ‘web design’?
The reason is, though you might be using the same word for describing, you are really talking about totally different things. That’s where the confusion comes in for people not close to the subject of web design, and all the variations.
What I’d like to do with this article is briefly go through all the component elements that go into web design to help give you a better sense of why there is such a big difference in cost with website projects, and where those costs come from.
Much like the Unuit and their many words for snow, you can get an in-depth understanding of the word ‘web design’ by understanding all of the different types of web design, and then apply that specialized knowledge to make the best decision for your web design needs. Ready? Here we go!
In this article, you’ll learn:
- Web Design Project Management
- Graphic Design – What Role Does the Graphic Designer Play in your Website Design?
- Branding – Or How you Want Your Audience to See You
- Marketing Strategy
- Information Architecture
- UX/UI Design
- Content Strategy – Was the Screenplay for Titanic Good or Bad?
- The Copywriter – Have you Clarified Your Message?
- Front-end Development – What the User Sees
- Backend Development
- Search Engine Optimization – How Customers will Find You
- Conversion Rate Optimization – Refining through A/B Testing
- Website Analytics and Conversion Tracking – How is Your Website Performing?
- Website Speed – It Counts for More than You May Realize
- Website Security – For yourself and your Visitors
- Website Server Deployment – Do you Have 500 visitors or 5 Million Visitors
- Frequently Asked Questions
Web Design Project Management

You’re probably familiar with the furniture company IKEA. Their profit model is based on transferring the cost of labor for assembling furniture onto the customer. Instead of paying workers to assemble the furniture they sell, the customer builds the furniture themselves. As a result, they’re able to sell furniture at a much lower cost than their competition.
The IKEA customer is not a skilled furniture builder, but they save on the cost of buying furniture that is constructed by experts. IKEA is a great analogy for how websites like Wix and Squarespace work. You get a cheap and affordable website, but effectively the quality is like IKEA furniture is in the furniture world. When you purchase a DIY website, you take on the role of the project manager, and in many cases every other role that comes with web design. Let’s take a closer look at the project management role if you were to defer it to a professional.
What is a Web Design Project Manager?
In the world of web design, the project manager manages every aspect of a web design project. They’re the person who makes the project happen. They effectively own the completion of the project and every step it takes to build the site from start to finish.
They manage everyone involved in the project from the writer, graphic designer, coders, and the client. The project manager must coordinate with everyone involved, keep the agreed-upon timelines, keep the project on budget, and make sure the client is happy with the end result. A good web design project manager will have enough experience in every phase of web design to know if the project is heading in the right direction. They can anticipate bottlenecks before they happen, and find solutions to hangups along the way to keep the project on pace.
Graphic Design – What Role Does the Graphic Designer Play in your Website Design?

Man is editing photos on laptop, using graphics tablet and interactive pen display, sitting at the table at cafe with cup of tea. Close-up.The next component of web design is graphic design and the graphic designer. Not too long ago the graphic designer was just a photoshop expert and only focused on that aspect of web design. Today, it’s still common, but more and more graphic designers are also front end developers.
A graphic designer is fundamentally a creative person. They tend to think abstractly, they’re messy, they’re pushing the envelope for inspiration and creativity. The creative process is not clean or conservative, the graphic designer is an artist. But, they also need to be able to understand design best practices and trends, and work within restraints.
What Makes a Good Website Graphic Designer?
Because of the sophistication of today’s websites, graphic designers need to be familiar with technical components like Javascript languages and understand how their design will interact with front end code. Graphic designers must design within the limitations of what is possible.
Typically with a website design project, you would have the graphic designer fully design the website independently from the technical coding aspect. Their job is to put together a visual representation of what the site will look like.
This means they will need to understand best practices for layout, fonts, typography, and all things graphic design related. They should know what’s going on at the moment in terms of trends and imagery and what layouts are getting the most traction among users. The ability to design for both mobile and desktop is critical. And of course, they must take this knowledge and skillset and create something beautiful and unique, but at the same time familiar.
Branding – Or How you Want Your Audience to See You

The terms “brand” and “branding” have been a part of the popular vernacular for the past several years. Branding is another way to talk about your identity, and more specifically, how you want people to think and feel about you or your business when they see your name.
Branding is about telling a consistent story in terms of messaging and design. There may be slogans that describe your brand promise. Particular colors or images may be associated with your brand image. The combination of these elements should create a familiar and positive feeling that your audience associates with – you – or your brand.
If you have established your brand identity you will want to incorporate it with the design elements and messaging on your website. All of your marketing materials online and offline should reflect your branding.
Marketing Strategy

Having a great website is only the first step. You need people to find it, and the right people. First, you need to understand who your target audience is, then target them through different marketing channels, and lastly put them through a sales funnel to convert them into customers.
Customer Avatars – Who is Your Audience?
If you’re not marketing to the right people it shouldn’t be a surprise when they don’t’ buy. A customer avatar or persona is a fictional version of your ideal customer. If you’re selling software for onboarding new employees then you’d create a customer avatar of a person that works in a company HR department and deals with new employee paperwork.
No matter who your customer avatar may be, the most important part is identifying their pain points. What do they need? What are they struggling with? Understanding their pain points can help you understand how you can present yourself as the solution.
Marketing Channels – How to Find Your Customers
You’ve identified your customers, but how will you get them to your website? You’ll have to find them online through various marketing channels.
- Social Media: If your customer avatar is a working professional you might find them on LinkedIn. Facebook is good for nearly all industries, and Instagram works for visually showcasing products and creating short videos.
- PPC Ads: Google Pay per click ads can get you on the top of the results page when prospects search for keywords that describe what you offer.
- SEO: Search engine optimization is a marketing strategy that strategically places keywords and keyword phrases into your messaging so people will find your website doing an organic search. For example, If you have a dental office in San Fransisco, you would want to show up on the Google results page when somebody types in the keyword “San Fransisco Dentist.”
- Email Marketing: Typically you get a prospect’s email address through your website through a lead generation magnet like a free PDF download. One they’re on your list you can market to them through email newsletters, educational blog posts, and direct offers on specials.
Offline you can still find prospects and drive them back to your website. If you find yourself attending trade shows and conferences giving someone your business card can lead to them visiting your website.

Sales Funnel – How to Make them Your Customer
Sales funnel is a term the describes the process of turning prospects into leads and then into customers. A prospect could be defined as a person who visits your website. If they’re looking at your website, they have some level of interest, but how much you don’t know.
A good website will incentivize prospects by offering some kind of free value. Often it can come in the form of a free guide that will better help them understand what they need. If your business is home remodeling you might offer a free guide with the title “10 Affordable Ways to Transform Your Kitchen.”
Once the prospect gives you their email address in exchange for the free guide, they are now a lead. How will you convert your new lead to a paying customer? Now that they’re on your mailing list you can email them more valuable tips and discounts. Having a strong and clear call to action increases the chances that the lead will eventually contact you giving you the opportunity to convert them into a customer.
Information Architecture
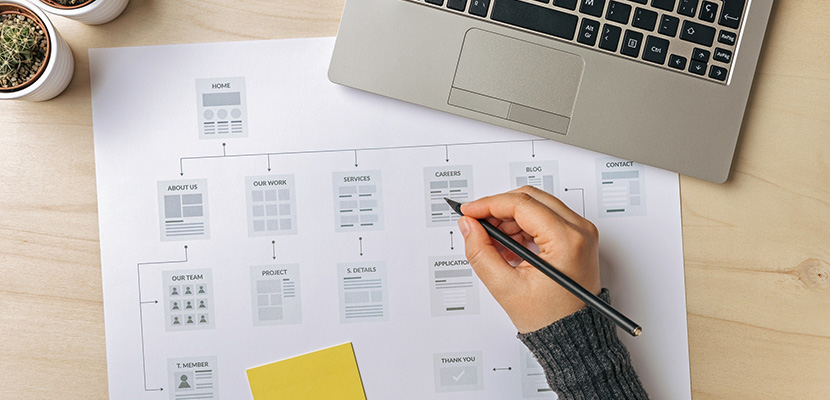

When you think of information architecture think of it as a non-technical blueprint for your entire website. Information architecture for web design is a tool to give you a snapshot of everything in an organized way.
Your website’s information architecture will include the structure of the content across your entire site – think where each page goes. It can also demonstrate the content structure within a page – think video goes here, text goes there, etc. Bigger, more complicated websites will even use color-coding to organize content and identify which user type the content is for to ensure all target audiences are covered.
Information architecture is influenced by your marketing strategy, UX/UI design, and content strategy.
UX/UI Design

The UX/UI design feels like a complicated and ambiguous term. It is and it isn’t. The main idea here is testing the user experience. UX/UI design is relevant when you’re building a website and the second phase comes when you test the website with real users.
UX design is in reference to the term “User Experience Design.”
UI design stands for “User Interface Design.”
User experience (UX) focuses on any interaction a user will have with the website. It considers all of the variables that shape the experience. How it makes the user feel, how easy it is for the user to accomplish their desired goals, etc. The (UI) aspect would focus on ensuring that each page visually communicates the desired interactions on a page.
In more simplified terms UX/UI design is about thinking like the person who would be interacting with the website. You’re trying to take out as much impediment as possible. Where is the friction? Where is it obvious that someone is looking for something and can’t find it? The only way to really identify bottlenecks is through testing with real users. Ultimately UX/UI design tests the hypothesis you made for the marketing strategy and information architecture phases of your website build.
Content Strategy – Was the Screenplay for Titanic Good or Bad?

You’re probably wondering why I’m talking about the movie Titanic here. Believe it or not, it’s a good analogy for good content strategy. Many critics rightfully pointed out how awful the dialogue in Titanic was. It was very cliched and far from natural. However, Titanic as a whole is a critically acclaimed movie that still holds up to this day despite the bad dialogue. Why?
Because Titanic had a great story structure. It was compelling and was constructed in a way that kept the audience engaged from beginning to end. It was a great story structure that made the movie work, and a good content strategy will do the same for your website.
Content strategy looks at the big picture and asks important questions. What are the main pieces of content? What are the main pages that we’ll be highlighting – and why? How about the order they’ll be presented? It’s similar to information architecture, but with more detail and singular focus.
Content strategy is Big Picture messaging strategy.
The Copywriter – Have you Clarified Your Message?

A copywriter is a professional writer. Copywriting is a very broad field, but many copywriters specialize in writing for web design. The word “copywriter” and sales writer are basically interchangeable for the most part. Sales copywriters get paid to write powerful headlines and text that motivate readers to take action and buy a product or a service.
Aside from the sales aspect, copywriters write informational copy (words) for a website where it’s needed. They’re not only selling, but they’re adding value by giving users the information they are looking for.
The biggest value a copywriter brings to web design project is clarity. Good writing looks easy, but it’s hard to accomplish. It’s a combination of skill and art. A good copywriter will take a complex topic, extract out what’s important, and make it easy to understand. Simplification and clarity is really the value a professional copywriter will bring to your web design project.
Many business owners are too close to their business and have a hard time talking about what they do in a non-technical jargon-free way. A copywriter will work with a business owner and ask them the right questions to get to the heart of what matters to their customers, then organize it and put it into words that work on their website – and motivate visitors to take action.
Front-end Development – What the User Sees

The front-end developer is the person who codes how the website looks. It involves everything related to CSS, HTML, the structure of the page itself, along with design, layout, and colors. CSS, HTML, and JavaScript are languages the front-end developer will be familiar with. Any kind of interaction that’s loaded on a page that does something is often done through JavaScript.
Another important task the front-end developer takes on is mobile design. The graphic designer will starts by designing a mobile-first design, then the front-end developer creates a mobile development framework to ensure the site will respond to all the different devices it may be viewed on.
Backend Development

As websites become more and more complex they movt into what are called web applications or web apps. They look like a typical website on the front-end, but the way they interact and function depend on software built into the back-end.
There are a lot of back-end development languages like PHP, Linux Apache, My Suite, and more. A website that can “do a lot” like Facebook, for example, will pull data from a backend database and then serve it back to the user using queries.
A more complex website the uses the back-end more might have a number of filters, shopping carts, etc. The basic idea is that websites that are processing large and complex amounts of data do it through backend functions.
A backend developer is the person that builds the backend so a website can execute all the desired functions. The more complex the functions, the better and more skilled the developer should be. Some of these websites might include hundreds or thousands of pages.
Search Engine Optimization – How Customers will Find You

SEO or search engine optimization is all about ranking and getting found through Google search. When a potential customer types in something you’re offering you want your website to show up in the search results.
SEO starts with keyword research. You want to find out the words potential customers are typing into Google when searching for the products or services you offer. If you’re offering financial planning services in San Fransisco you might want to rank for the keyword phrase: “financial planner San Fransisco.” There are dozens, if not hundreds of related keywords in your specific industry that you can rank for. One strategy is avoiding the super competitive ones and trying to be number one is a less difficult keyword – at least when you’re starting out.
In addition to keyword research, SEO involves properly tagging the pages on your website to optimize for the keywords you find. It also involves optimizing the content on your website using best SEO practices so Google can index your pages appropriately and help customers find you.
Conversion Rate Optimization – Refining through A/B Testing

Once a website has launched and people are seeing it, for many companies, the project is far from over. Conversion rate optimization is the process of putting different versions of a website out and comparing the results using A/B split testing.
For example, website version 1 might have a different headline than website version 2. The test is to see which website performs better with the different headline. There are different metrics you can use to test success such as bounce rates, or sales. But it doesn’t just stop at headline variations. You can try different colors and messaging – really anything.
Conversion rate optimization is the norm for big companies. They have the money to continually test and they do. To get an idea of how a website can evolve over time using conversion rate optimization there’s a free online tool called the Wayback Machine. Type in the URL of any website and you can view all of the past versions.
Website Analytics and Conversion Tracking – How is Your Website Performing?
Website analytics and conversion tracking is a way to get data about how your website is performing. There are a number of tools to track data, and just as many experts that make a full-time living as analytics experts. Big companies have in-house experts that focus solely on analytics and make recommendations based on what they find.
Even small companies that can’t afford to hire a full-time analytics expert can benefit from knowing what their website is doing. How you use website analytics is very scalable. It can be as basic as knowing how many people are visiting your site. If you’re not getting the traffic you want, then that one data point would inform you that you probably want to evaluate your SEO.
Website Speed – It Counts for More than You May Realize

How fast does your website load? You might not think that a few seconds would make any difference, but it can be a deal-breaker for users and Google.
The load time of your website greatly impacts your results in Google search rankings. For every second your site loads slower, you lose 10% on your conversion rate in the eyes of the Google algorithm. It’s a big deal.
What Goes into Website Speed?
A lot of things. Image sizes affect your JavaScript load times. Redirect calls. Each time a page redirects to another page, your visitors have to wait for the HTTP request-response cycle to complete. Aside from your website itself, the server you use affects your website speed. Depending on how much traffic your website gets determines the server you’ll need to use.
Website Security – For yourself and your Visitors

More and more people and businesses are getting their websites hijacked and held for ransom. It’s critical if you have sensitive information, are transmitting sensitive information, or just like your website and want to keep it that you protect it with the appropriate security software.
There are a number of affordable security certificates that can be integrated into your web design to ensure that your site stays protected.
Website Server Deployment – Do you Have 500 visitors or 5 Million Visitors?

A big part of web design is designing for today and the future. Scalability needs to be built into your design. Thankfully there are services today like Amazon Web Services that make this much easier than it used to be. If you use a proven CMS like WordPress then you can actually scale much more easily than only a few years ago.
Just as important as scalability is your website server. Your server is completely separate from your website – it’s your website’s virtual home. The server is doing a lot of functions on the back-end of your website. Website hosting is an entire industry with hosting experts who manage sites and servers full-time. Determining the right hosting provider for your website is an important part of the web design process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a Web Designer and a Web Developer?
Think of the web designer as a graphic designer. They’re the creative person who makes the design look beautiful. They add the content, pictures, and imagery always keeping the user experience and how they might feel in mind.
The web developer is the person who does the coding on the website. They code the CSS, HTML, and turn the visual framework the web designer creates into a functioning website. Think of the web designer as the architect and the web developer as the builder that brings the blueprint into something that can be used.
What Does a Web Designer Do?
A web designer may do everything we’ve mentioned in this article, especially if they’re a freelance do it all themselves kind of web designer. They’re doing graphic design, some branding, coding, server work, SEO, copywriting, and project management. In this case, they’re doing A LOT.
What I think about in terms of web design and web designer is a person who is a front end designer. Someone who is essentially making the design and thinking about layout, fonts, colors, topography, and style. When you hire a web design company that has a team fulfilling all of the different roles, that’s what a web designer does.
Web Design Examples
Believe it or not, the last thing you want to do when thinking about web design is go check out your competitors’ websites. If you’re going to look anywhere for inspiration look at the best websites in the world. Websites that get the most traffic. Websites like Amazon for example. They probably have millions of pages packed into a simple and easy to navigate design. They know how to communicate to a person that’s looking to have a particular problem solved – and you should take the same approach with your website. Your website is an online marketing tool, so learning from the best at online marketing is the smart thing to do when looking at web design examples.
What is Meant by Web Design?
Web design is really about thinking about the process of problem-solving for your audience. Once a visitor is looking at your website your job is to communicate to them that you’re the person or business they’ve been looking for to help solve their problem.
Websites are about people first, and that should always be at the top of your mind in the web design process. A web designer, if they’re any good, will always work from the theme of who is the customer, what are they looking for, and what is the next step they want to take. That is the heart of good web design.
How Long Does it Take to Build a Website?
A website can take one day to one year to build… What determines the time is the complexity and originality of the design. Are you creating a new original design or using a template? Is the content new, or are you using existing content? How many cooks are in the kitchen? The more people involved in the decision making, the longer it takes. There’s a lot that goes into determining how long it takes to build a website.
What is the Main Focus of Web Design?
At the end of the day, the main focus of web design is a human being that’s looking to solve a problem, answer a question, or learn something new. Your focus is to identify the problem and communicate in such a way that helps that person get closer to solving their problem. Everything else is meant to facilitate that. Additionally, you’re trying to turn solving that problem into profits for your business. You’re trying to position yourself as the best problem solver in your industry.
Is Web Design Hard?
Yes, it’s super hard. You’re basically trying to create harmony out of chaos. You have to know a million things at once, and all of those things keep changing all of the time. There’s always new software, new tools, new methodologies, best practices, etc. You’ve probably heard that technology advances an and exponential rate – the same goes for web design. In addition to technology, you’re working within multiple different disciplines like graphic design, psychology, and statistics, just to name a few.
What is the Process of Web Design?
The process starts with trying to create a basic structure that will become your sitemap. Your sitemap identifies what pages will be on the site, and where. Whether it’s a 10 page or 10,000-page site, you want to get clarity on what it is and where it goes.
After the sitemap, you can create an initial design around that framework, and then create content for it. You need content for every page on a website. After that, you need to redesign and fine-tune around the content making sure it fits visually and is user friendly. Then you start coding and bringing the website to life. Here is a more in-depth breakdown of the web design process.